This content is also available on YouTube and Spotify:
Introduction
IT is the hardware and software to connect thousands of devices in a network and manage their exchange of information. The purpose is to enable data storage and its usage for business and operations. Tasks range from connecting simple telephones to managing complex global networks.
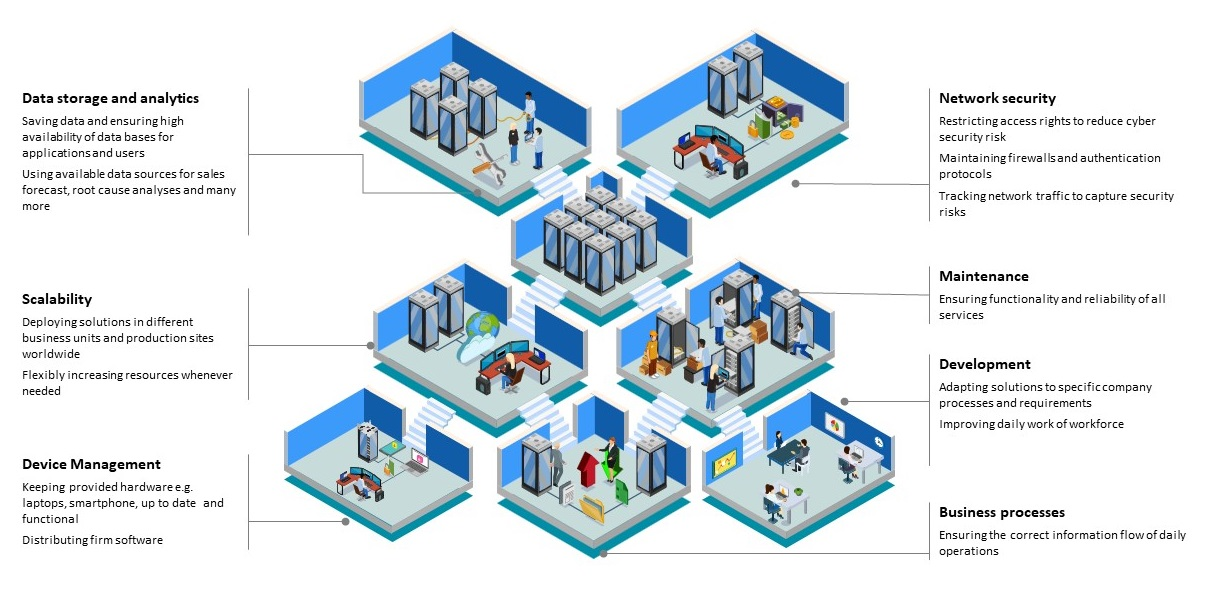
As you can see, the field of IT spans a wide range of topics, ranging from data and device management, over security and scalability concerns to development and maintenance.
Typical responsibilities:
- Setting up phones, PCs, printers and other office hardware
- Monitoring devices and networks for security breaches
- Maintaining local servers
- Configuration of business systems e.g. ERP/SAP
- Updating devices to ensure IT security
- Setting up local networks and Wi-Fi
- Implementing business solutions like automation
- And many more…
Typical vendors:
What is important in IT?
Nobody wants to build an app for years just so that the end-user removes it within 30 seconds
We will see the exact same chart later in the next chapter related to Operational Technology(OT).
High importance
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Quick development cycles, e.g., agile | Good user experience is more important than a perfectly designed app |
| Scalability | Apps need to handle millions of users at the same time (e.g., Google, Netflix) |
| User experience | If something is unintuitive, people tend not to use it |
Of lesser importance:
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Reliability & Safety | Hardware is redundant, if one fails another can take over; Consequences of hardware failures are smaller |
| Maintainability & standards | Standards are usually best-practices and might change over time. No hard-written norms. |
| Certifications | Therefore, certifications are not legally required |