Network issues can be frustrating and difficult to diagnose, but there are a few basic checks you can perform to identify the problem. Before diving into more complex troubleshooting steps, it's important to ensure that the physical connections are secure and that the cables are working properly.
Instructions
General
- Check Physical Connections: Ensure that the cables are properly connected and check the LEDs on both sides of the cable, which should be blinking if there is a successful connection.
For Windows
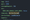
Network Configuration: Open the Command Prompt and run the command ipconfig /all. Search for your network adapter, such as Ethernet, to view your current MAC, IP, DNS, and Gateway configurations.
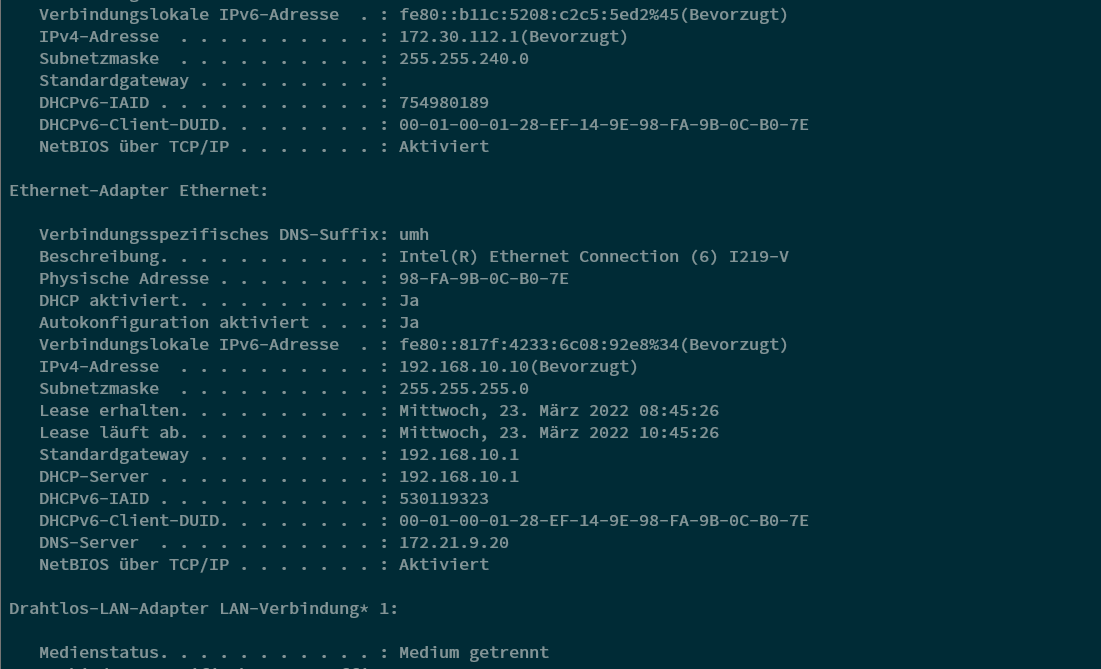
Test Internet Access: Run the command ping google.de to check for general connectivity to the internet and your DNS settings.
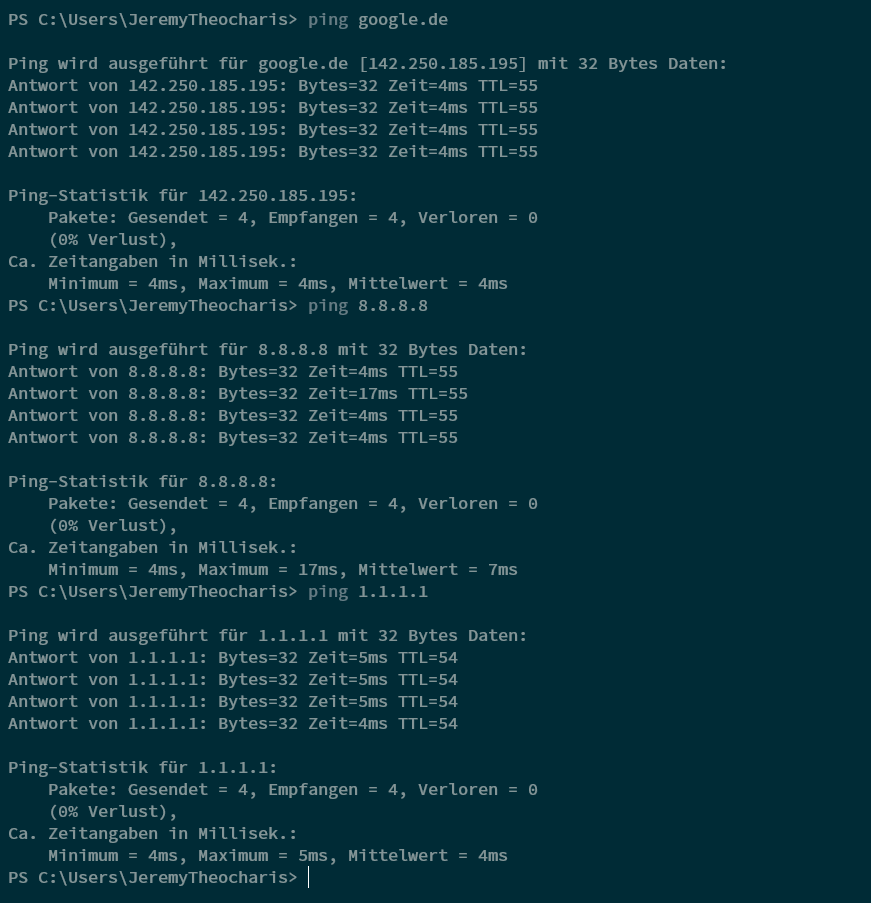
Verify DNS Settings: Run the command nslookup umh.app to verify that your DNS settings are set up correctly.
For Linux
- Network Configuration: Open the terminal and run the command
ip addrto check the network configurations. - Test Internet Access: Run the command
ping google.deto verify that you have internet access. - Verify DNS Settings: Run the command
nslookup umh.appto check if your DNS settings are set up correctly.